StarWind Virtual SAN Asynchronous Replication. Configuration Scenarios
- Guidance
- January 23, 2019
IMPORTANT NOTE: Starting from 14869 build, the Asynchronous replication feature was excluded and deprecated. Please remove all Asynchronous replicas and LSFS devices before the update. See more information in the release notes: https://www.starwindsoftware.com/release-notes-build
INTRODUCTION
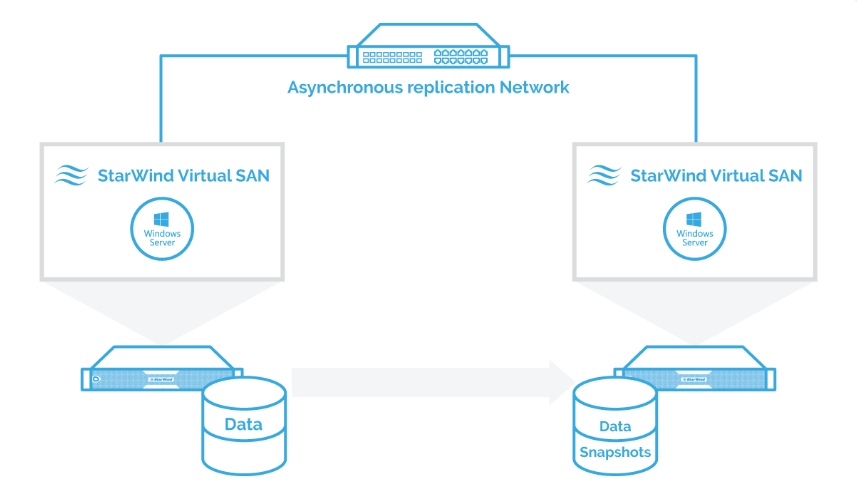
Asynchronous Replication is used to create an independent copy of data and store it separately from the main storage system. It allows users to restore data on the primary site which has suffered from a virus attack, disaster, or erroneous human activity. It is the backbone of backup and Disaster Recovery processes. The Replication process can be scheduled in order to prevent the main storage system and network channels overloads. The Replication process usually is scheduled outside production hours, so that it doesn’t interfere with the primary workload.
Snapshots, being saved “states” of the system at given time, play significant role in Disaster Recovery and backup processes.
The snapshots created with StarWind VSS provider are guaranteed to be consistent. StarWind VSS provider is a proprietary software designed for internal Virtual SAN usage and should not be used for any purposes externally. It serves snapshot-supported devices, i.e., LSFS or Asynchronous Replication.
Asynchronous Replication can work through network channels that are significantly slower than the ones used for connection of the storage system.
Main Asynchronous Replication configuration scenarios
Automatic Replication
If automatic replication mode is configured, the system works by the following algorithm:
- Create a snapshot of the main storage
- Transfer the snapshot to the replication site
- Delete the snapshot on the main storage, if necessary
- Delete the oldest snapshot on the replication site, if necessary
NOTE: During the snapshot creation, StarWind VSS provider can be used depending on the initial replication configuration. If it is configured, please make sure that StarWind VSS provider also is installed on the replication site. The number of snapshots kept on the main storage can be different from their number on the replication site.
Backing up with third-party utilities
Snapshots operations are usually performed through the VSS mechanism using VSS provider. In this way, the backup software uses snapshots by the following algorithm:
- Create a snapshot of the main storage
- Mount the snapshot
- Copy data from the snapshot to the repository with its mechanism
- Unmount the snapshot
- Delete the snapshot
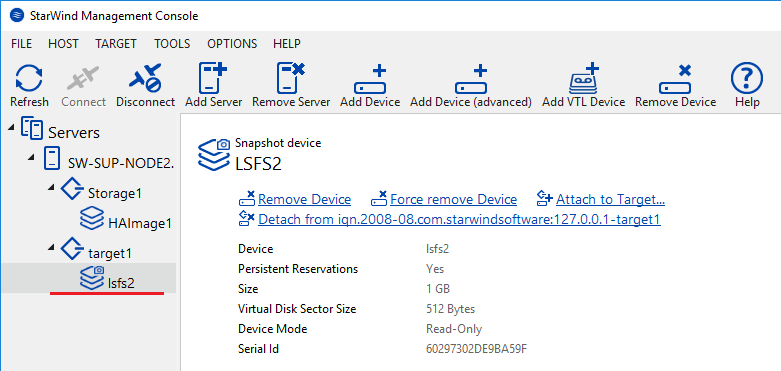
Checking the status of the replicated data, selective data recovery
It is recommended to regularly check the data consistency of the snapshot/backup. The easiest way to check for consistency is to read from the snapshot once it was created and compare the data in the source snapshot. The snapshot has to be mounted, thus an additional target is created on the asynchronous node.
Also, it may be necessary to access the snapshot in order to recover the certain files without changing the state of the main storage. For that purpose, the snapshot needs to be mounted from the asynchronous node to the local one. After mounting the snapshot, the administrator can access the storage in the “read-only” mode. Note that the mounted snapshot can cause conflicts with the main storage within the OS. This can be avoided by substituting the “VolumeId”.
Full Device recovery from the snapshot (back seed)
Choose the recovery point (snapshot) and start the recovery process on the main storage.
NOTE: During the back seeding procedure, the initial data (the data that was in the main storage before this process started) on the main storage will be lost. During back seeding, data can be copied from the selected snapshot only.
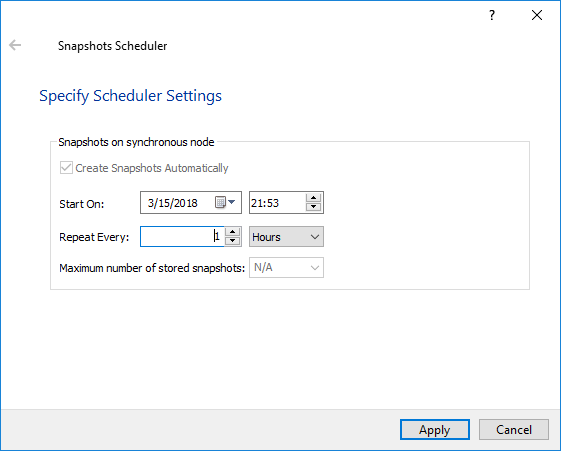
Snapshot Scheduler during the replication process
Snapshot Scheduler initiates the snapshot creation process, deletes the old (outdated) snapshots, enabling to store the specified number of snapshots on the storage.
Asynchronous Replication implemented with LSFS device and ImageFile device
Log-Structured File System (LSFS) is a proprietary file system, designed by StarWind for better virtualization workloads handling.
LSFS provides the integrated LSFS snapshots stored with the main LSFS device data.
While working with ImageFile, the additional instance, data change log, is used. As a storage for the data change log instance, the separate storage is used. Note that this storage needs to be segregated from the main one. Storage for the data change log instance can be chosen in the Asynchronous Replication setup wizard.
All new data will be initially written to the to the data change log instance, with its following transfer to the main storage in the background.
CONCLUSION
By configuring Asynchronous Replication in StarWind-based infrastructure, users can take advantage of backup and DR functionality. By taking snapshots of the system “state” and sending them to a remote site (for example, public cloud), it becomes possible to restore normal operation after its unexpected disruption. With an effective snapshot schedule, the data loss and failures consequences can be effectively prevented.